Hedges: location and care
Post from EditorialsBefore making a hedge you must study the location for planting, so stick to compliance with legal constraints and local regulations.
The boundaries of the garden
 Delimiting a garden can be a moment of pure creativity if instead of the usual fence or gate you choose to organize a whole plant boundary, surrounding your property with a vegetation dune, interrupted only by the steps of access.
Delimiting a garden can be a moment of pure creativity if instead of the usual fence or gate you choose to organize a whole plant boundary, surrounding your property with a vegetation dune, interrupted only by the steps of access.
It is thus to create an oasis of greenery that isolates us from the outside view, creating at the same time the right privacy.
Before creating our hedge is important to study well the location for the planting of trees or shrubs, so stick to compliance with legal constraints and any local regulations.
Only then we can decide which plants will form the fence and what are the precautions essential for it to grow evenly and in the desired shape.
Legal issues
In the formation of a hedge you must first take a look at the distances of wood species that according to the Civil Code must be respected to safeguard relations with neighbors.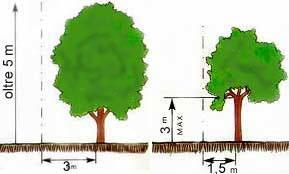 - Tall trees such as walnuts, chestnuts, cypresses, poplars, oaks, pines, elms and plane trees: 3 m away from the border.
- Tall trees such as walnuts, chestnuts, cypresses, poplars, oaks, pines, elms and plane trees: 3 m away from the border.
- Trees of medium height and trunk that is, for those with no more than 3 meters: 1.50m away from the border.
- Trees, shrubs and fruit trees of height not exceeding 2.50 m: 50 cm away from the border.
The measures to be taken horizontally and from the boundary up to the side of the trunk closer to this, at the time of planting.
The hedges should not exceed 2.50 m in height and must be planted at 50 cm from the border. For hedges wider alder type, chestnut, hornbeam, beech, the distance increases to 1 m from the border.
WARNING: the distances do not have to be observed on the border if there is a partition wall, as long as the plants are required to height that does not exceed the top of the wall.
Planting the hedge
The best time to plant a hedge is between the BEGINNING of fall and the BEGINNING of spring, with preference for the month of April in the town with cold weather.
The soil should be prepared at least one week before.
If you need to buy the plants it would be better to place your order earlier. This means making in advance all the necessary work on the ground. The planting of hedges requires the realization of a small trench, ie an excavation along the path you want to fill with the hedge.
The planting of hedges requires the realization of a small trench, ie an excavation along the path you want to fill with the hedge.
In general, for the purposes of geometric regularity, the trench should be equidistant at all points from the border. In the absence of physical references it can be defined as a reference imaginary lines that can then be plotted using a rope stretched between two stakes driven into the ground.
The amplitude of the trench excavation, must be proportionate to the development of the roots of the hedge.
Almost always for the excavations are sufficient depth and width of two feet for shrubs and bushes; in the case of small trees hedge, must be at least one meter.
Of course, the width of the trench should be increased proportionally to the number of files to be carried or implanted. In general, the alternating arrangement of the plants, in addition to ensuring a greater compactness of the hedge, allows a saving of space compared to other provisions.
The hedge plants rely initially well aligned in the trench made, using the rope stretched between the poles of reference. Continuing in this way, as will be planted all plants.
The number of plants needed to form the hedge depends on their development and vigor. It is recommended to plant young plants and not too developed, having the patience to wait for their growth.
In the phase of planting you need to mix the filling earth with a lot of manure, at least 3 or 4 shoveling of manure for each plant.
Once finished the planting you need to water abundantly.
Essences and routine maintenance of the hedge
The hedges are divided into:
-high
-short
-junior high
-ever green
-suitable to coastal marine and mild climate
The classic species of plants for the hedge are: junipers, the aucuba and pittosporum. Very nice are also thuja, laurel and rosemary.
In order to keep the vegetation in the best conditions and geometric shapes, hedges require regular interventions at least a couple of times a year.
These have the purpose of controlling any excess development of the branches beyond the defined regularity, keeping the desired height. By pruning you obtain the effect of facilitating the emission of leaves and new shoots even in the lower part of the hedges.
The pruning and lopping are operations intended to remove the portions grown in excess of the twigs and maintain well leveled at different heights which define the geometry of the plant.
To fix the fence so that it is thick and with the desired shape is necessary to plant the shrubs at close range, and have the patience to trim it, from the second year, the highest branches in order to stimulate the growth of the lower buds.
So the hedge will be more dense and compact too close to the ground. The operations of shearing and pruning hedges often simultaneously cover large areas of one or more plants.
This extensive work can be carried out using special hand or electric tools.
To achieve a certain uniformity are made references tending some parallel ropes inside the jets overflowing.
It may take several pruning techniques, depending on the goals.
If you want to keep the thickness of the plant then you need to work laterally; if you want to increase the thickness of the hedges is by cutting off several inches in height.
It should be noted that to obtain an increase of height of the hedges, the extension must be accompanied by a denudation of the foliage of the plants and in the lower part of the stems.
For this type of operation should not be in a hurry to get a high hedge, but you have to intervene during the rest of the plants.
The action is that of a drastic pruning that slim the structure of the main branches and which has as a consequence the awakening of the gems shows in this way closer to the light.
Pruning is almost always required in addition to resize the plants, also to remove damaged branches and to penetrate the light even in the inner parts of the hedges.
A significant aspect for hedges is regularity or frequency of the spinning consists of more plants of the hedge. In general, these characteristics depend on the load capacity of the individual's species or plants of the hedge and the environmental conditions.
The mild temperatures and adequate fertilization stimulate, after every action of pruning and/ or topping, the vegetative growth. In principle, one can think to intervene with these actions whenever the new shoots of foliage of the hedge reach tens of centimeters from the predetermined line of spinning.
To get the perfect shapes, we can build a cage with bamboo canes woven and coated with light metal mesh, large mesh, so only prune the branches that grow over the net.
79870 REGISTERED USERS










