Hypocaust stove
Post from EditorialsWarming up with an old technology mixed with modern materials is now possible, here is the new tiled stove with hypocaust heating system.
What does hypocaust mean?
By definition, hypocaust is the plant that was used by the ancient Romans to heat the rooms. The system was very simple and consisted in making circulate under the floor and in the cavities of the walls hot air coming from a source, usually an oven, which contained the appropriate pipes intended for the elimination of fumes produced by combustion.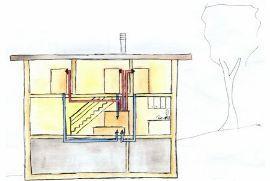 The more the fire in the furnace was greater the more intense was the heat distribution within the various environments.
The more the fire in the furnace was greater the more intense was the heat distribution within the various environments.
In virtue of this antique way of heating, in 1970 this technology has been taken up in the projects of heating of single-family homes, obviously making all possible innovations in the technical field and looking to expand the use of the ancient storage stove but improving the results especially in terms of comfort.
Structure and benefits of a hypocaust heating
Since ancient times the benefits of using this type of heating were well known, in fact this was often used as it had beneficial effects on the climate of the interior.
This characteristic is closely dependent on the type of structure that represents an hypocaust heating system.
In fact the hypocaust heating system needs a raised floor, placed on pillars made in brick, and walls with an air space, spaces within which are conveyed the fumes produced by a wood-burning furnace. The basics of operation is similar to that of a fireplace with its exhaust pipe.
The core of the system is just a firewood furnace used for the production of hot water, for baths. The smoke produced by burning wood in the furnace came out of this through one or more openings heading towards the channels made in masonry which were placed under the floor of the rooms to be heated.
The smoke produced by burning wood in the furnace came out of this through one or more openings heading towards the channels made in masonry which were placed under the floor of the rooms to be heated.
These same fumes were coming out thanks to interspaces practiced in the double walls of the premises, so as to make it assume the function of real radiant walls.
Using this system, it was ensured an uniform heating of all rooms of the house, and also using a sustainable technology, as based on the method of operation of a simple fireplace.
Tiled stove with hypocaust heating system
The tiled stoves, both for their beauty, and for their functionality, are sometimes preferred to conventional heating with heaters.
The amount of heat that is released into the environment by this type of stove is remarkable, since it consists of not only the heat radiated from the heater, but there will also be a certain part of the heat transmitted by convection.  The quantity of heat transmitted obviously is strictly dependent on factors such as the thickness of refractory clay and the length of the forced draft, this determines the formation of the warmest areas on the surface of majolica, leaving instead some areas of the stove colder. This thing depends precisely on the fact that the hot air stream that moves inside the fumes channel, transmits heat to the same channel through the conduction.
The quantity of heat transmitted obviously is strictly dependent on factors such as the thickness of refractory clay and the length of the forced draft, this determines the formation of the warmest areas on the surface of majolica, leaving instead some areas of the stove colder. This thing depends precisely on the fact that the hot air stream that moves inside the fumes channel, transmits heat to the same channel through the conduction.
The tiled stove then due to its structure will always have areas with different heating degrees. As a result of this uneven distribution of heat may create cracks within the structure of the stove.
One way to clear this problem is the use of the hypocaust heating system but always using a tiled stove.  To achieve it we use segments of ceramic. Is important to know, however, that before installing the various elements in ceramic, the rear wall of the stove must be insulated with special panels.
To achieve it we use segments of ceramic. Is important to know, however, that before installing the various elements in ceramic, the rear wall of the stove must be insulated with special panels.
If you were to compare an hypocaust heating system with a normal stove, you would noticed substantial differences: first of all the presence of air space between the elements of construction and the refractory clay of the outer wall.
These spaces have dimensions that are always different, depending on the space they occupy and depending on the size of the stove. The basics of heat transfer this time is no longer the conduction, in fact there is no contact between the various elements but by radiation.
The internal structure of the hypocaust heating system is constituted by refractory elements of connection for the passage of fumes and by gaps, in this way, being the whole structure closed, the heat is transported from warmer surfaces to colder areas through natural thermal convection. The tiled surface that is heated is much bigger than a normal stove that does not include the hypocausts system. The various hypocaust stoves are designed in function of the quantity of heat to be obtained, of course, if the surface to be heated is greater, the temperature on the surfaces will be lower, compared to the same heater placed in an environment less extended. In this way it has a heat diffusion inside the environments more homogeneous, creating a pleasant feeling of well-being for the people who live those spaces.
The various hypocaust stoves are designed in function of the quantity of heat to be obtained, of course, if the surface to be heated is greater, the temperature on the surfaces will be lower, compared to the same heater placed in an environment less extended. In this way it has a heat diffusion inside the environments more homogeneous, creating a pleasant feeling of well-being for the people who live those spaces.
When you realize the design of a stove with a hypocausts system, you must pay close attention to the materials used, because inside this structure pass very high temperatures gasses; using the wrong materials would lead to serious problems for both the facility and the environment.
A company that takes care of the production of building materials suitable for the achievement of the hypocaust systems is ORTNER.
Other companies increasingly widespread in the industry are Schmid and Candrac.
79778 REGISTERED USERS










